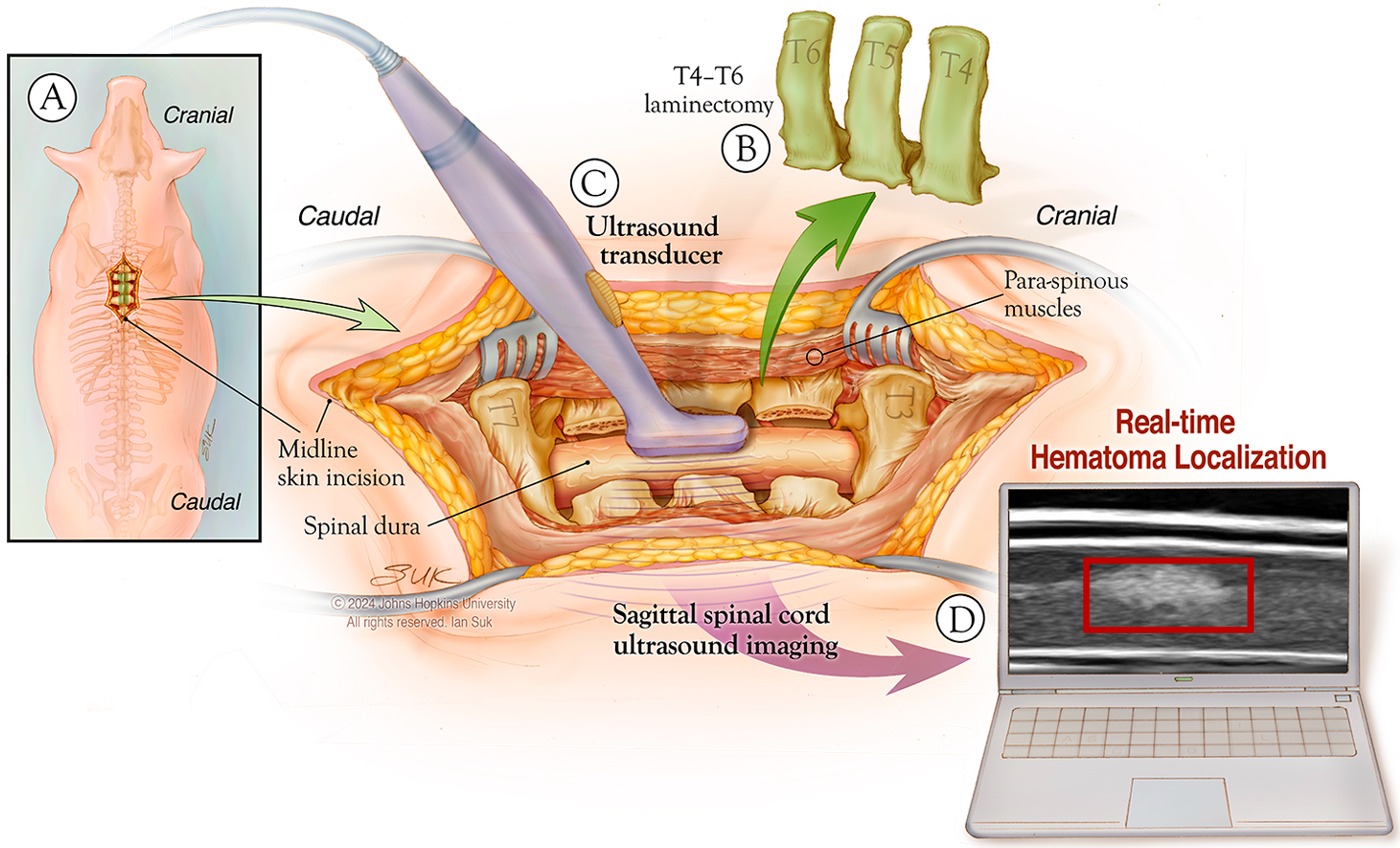
A novel open-source ultrasound dataset with deep learning benchmarks for spinal cord injury localization and anatomical segmentation
Avisha Kumar, Kunal Kotkar, ... Nicholas Theodore, Nitish Thakor, and Amir Manbachi
Published in: ArXiv
paperHere, you can find links to my papers and prepints.

Avisha Kumar, Kunal Kotkar, ... Nicholas Theodore, Nitish Thakor, and Amir Manbachi
Published in: ArXiv
paper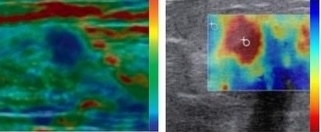
Abstract: Tissue elasticity remains an essential biomarker of health and is indicative of irregularities such as tumors or infection. The timely detection of such abnormalities is crucial for the prevention of disease progression and complications that arise from late-stage illnesses. However, at both the bedside and the operating table, there is a distinct lack of tactile feedback for deep-seated tissue. As surgical techniques advance toward remote or minimally invasive options to reduce infection risk and hasten healing time, surgeons lose the ability to manually palpate tissue.
paper
Abstract: While significant advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have catalyzed progress across various domains, its full potential in understanding visual perception remains underexplored. We propose an artificial neural network dubbed VISION, an acronym for “Visual Interface System for Imaging Output of Neural activity,” to mimic the human brain and show how it can foster neuroscientific inquiries. Using visual and contextual inputs, this multimodal model predicts the brain’s functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) scan response to natural images.
paper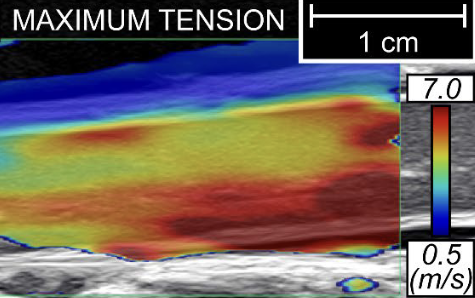
Abstract: Background: Tension in the spinal cord is a trademark of tethered cord syndrome. Unfortunately, existing tests cannot quantify tension across the bulk of the cord, making the diagnostic evaluation of stretch ambiguous. A potential non-destructive metric for spinal cord tension is ultrasound-derived shear wave velocity (SWV). The velocity is sensitive to tissue elasticity and boundary conditions including strain. We use the term Ultrasound Tensography to describe the acoustic evaluation of tension with SWV.
paper
Abstract: Focused ultrasound (FUS) is an increasingly prevalent therapeutic tool used in medicine to treat patients non-invasively, cost-effectively, and without any ionizing radiation. Depending on the clinical application, therapeutic ultrasound can be used for tissue ablation, physiotherapy, lithotripsy, and drug delivery, among other therapies. For the treatment to be effective, it is important to understand the acoustic pressure profile in the tissue to ensure the focal point intensity is sufficient to achieve therapy without damaging the tissue.
paper